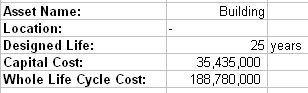
Whole life cycle cost is the total costs of the asset throughout its life cycle from its acquisition until disposal, amongst others includes:
Whole life cycle cost is important in order to determine the actual cost that will be incurred in the future, the benefits that will be derived, the cost of operation and maintenance, the capital expenditure needed and so forth. Previously, we would be satisfied if we only know the capital cost as it is the easiest to do, but it is not the true cost of the asset.
Cost of the assets relates to the design and shape of the asset, the equipment employed, the type of material used, type of operation and maintenance deployed and so forth. Before making justifiable and the right decison, an organization needs to know all costs, which become future liabilities. These liabilities would cut into the profit margin and the organization will be non-profitable for the asset it holds. This scenario is not a good business case if the organization needs to venture and explore new business areas.
Nevertheless, if an organization acquires the predicted costs of actually having the asset, then a predicted cast flow is known throughout the asset life span, which can span more than 25 years. A good business decision is ensured and the decision to acquire the asset is well justified.
Capital cost
Cost of the assets relates to the design and shape of the asset, the equipment employed, the type of material used, type of operation and maintenance deployed and so forth. Before making justifiable and the right decison, an organization needs to know all costs, which become future liabilities. These liabilities would cut into the profit margin and the organization will be non-profitable for the asset it holds. This scenario is not a good business case if the organization needs to venture and explore new business areas.
Nevertheless, if an organization acquires the predicted costs of actually having the asset, then a predicted cast flow is known throughout the asset life span, which can span more than 25 years. A good business decision is ensured and the decision to acquire the asset is well justified.
Capital cost
Capital costs, amongst others, include:
- Design and supervision cost
- Cost of acquiring or purchasing land
- Interest and funding cost
- Construction or installation cost inclusive of all electrical
and mechanical facilities, incidental equipments and others - Cost of permits, levies and approval from local authorities
- Project management costs
- Consultation cost
Operating costs are cost incurred when operating or using the building, amongst others, include:
- Telecommunication bills or usage
- Electricity bills or usage
- Gas, Water and sewerage bills or charges
- Chilled water bills or usage
- Tenancy fees or charges
- Local authority or central government taxes or duties relating to the
property - Insurance and tax costs (if relevant)
Maintenance costs are costs incurred to ensure that the building functions as designed and costs to upkeep the building, such as:
- Custodial and up keeping
- Routine maintenance
- Unplanned or breakdown maintenance
- Planned or scheduled maintenance
- Security services
- Unplanned or planned inspection and assessment costs
- Special arrangements
- Increase in insurance, mortgage or interest rates
- Mitigation costs
Rehabilitation costs
- Installing new technologies within its functional life
- Major maintenance works to meet new customers’ demands
Administrative costs
- Management cost
- Direct and indirect costs relating to the management of the
asset and et cetera
Depreciation and disposal costs
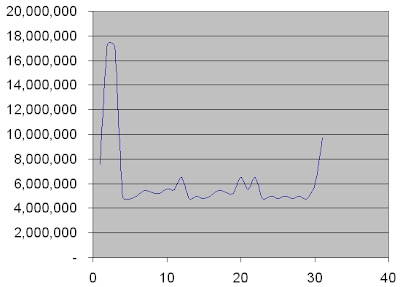
Typically, a whole life cycle cost curve will look lik this:
- Renewal cost inclusive any design, demolishing, and et cetera
- Disposal costs
- Replacement cost
- Depreciation cost
No comments:
Post a Comment